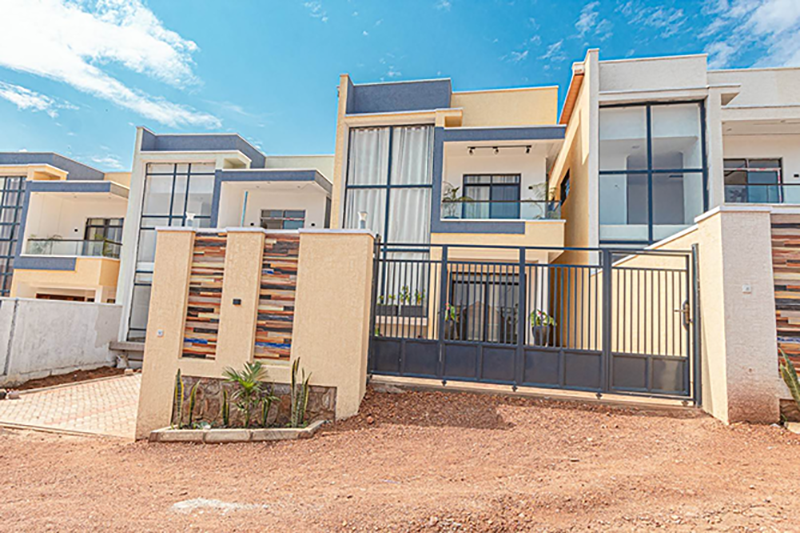
Rwanda is undertaking one of its most ambitious housing initiatives yet: delivering over 10,000 affordable homes by 2026, led by public-private partnerships in cities like Kigali, Musanze, and Rubavu. This large-scale project aims to meet growing housing demand and reshape the future of Rwanda affordable housing.
Why Rwanda launched this urgent housing program
Rapid urbanization, a rising middle class, and growing youth demographics created a critical need for increased housing stock. The government responded with a comprehensive affordable housing strategy targeting lower- and middle-income families. Rwanda affordable housing projects are designed to be cost-effective while maintaining quality and integration within planned urban extensions.
Key Features of the Housing Program
1. Public-Private Collaboration
Private developers build singles, duplexes, and townhouse units under standardized designs, bundled with government subsidies. Beneficiaries access Rwanda affordable housing through structured mortgage has been made more accessible via cooperative savings groups and soft loan programs.
2. Locations with Opportunity
The first wave of developments is in Kigali suburbs (such as Kinyinya, Gikondo, and Gahanga) and regional towns like Musanze and Rubavu. These zones were selected due to proximity to jobs, infrastructure upgrades, and land availability—making Rwanda affordable housing both practical and scalable.
3. Pricing and Ownership Structure
Sale prices for these homes start significantly lower than comparable market units—often between USD 15,000 and USD 25,000 depending on zone and unit size. Ownership models include rent-to-own and tiered mortgage plans over 10–20 years, making Rwanda affordable housing realistic for public and private wage earners.
What this means for home buyers and investors
Improved Access to Formal Mortgage Housing
For many middle-income families, this scheme opens the door to formal homeownership without the need for large gratuities or unstructured co-ops. Secure titles and standardized layouts help build equity at modest premiums.
Potential For Investment Returns
Some investors are partnering with developers to offer rental management on these schemes—yielding consistent rental income in suburbs with growing occupancy. While units are primarily for owner-occupiers, the broader growth in these zones can boost surrounding property values, benefiting nearby owners and small-scale investors.
Urban Planning & Amenities
These projects feature basic amenities: cornerstone services like reliable water supply, electricity, plus community schools and health centers. The focus on Rwanda affordable housing corridor development ensures neighborhoods are livable and sustainable.
Important Considerations Before You Apply or Invest
- Confirm eligibility: Applicants must meet income criteria, fitness requirements, and local residency conditions.
- Understand financing terms: Some units rely on government-subsidized loans or cooperative investments with specific repayment expectations.
- Research location zoning: Know your plot boundaries, future infrastructure plans, and local bylaws before committing.
- Plan for long-term resale or rental: Rental activity in these estates is still emerging; understand resale rules if buying for investment.
Final Thoughts
The rollout of Rwanda affordable housing, with over 10,000 homes expected by 2026, marks a turning point for accessible urban housing and mixed-income neighborhood development. For qualified buyers, this offers a pathway to equity and asset building. For investors, emerging rental demand and corridor development offer future upside.
To explore eligible listings, investment-ready plots, or get detailed guidance on Rwanda affordable housing, visit African Property Portal’s Rwanda section.
Are you planning to apply or invest in Rwanda’s affordable housing program? Share your questions or experiences below—your contribution could help others navigate Rwanda affordable housing options with confidence!